GLOSSARY
Data Breaches: How They Occur and How to Prevent Them
A data breach occurs whenever sensitive data is unintentionally exposed. It also occurs when an unauthorized entity leaks, or steals it. Breach events can happen by accident, through negligence, or they can result from a targeted attack.

Data breaches are invaluable to understanding a threat actor’s goals and motivations. Malicious actors, as well as Advanced Persistent Threats (APTs), will do whatever they can to gain illegal access into susceptible organizations. They employ a wide array of underhanded tactics. Examples include phishing or exploiting vulnerabilities. They are often fueled by financial gain.
Studying breach events can help CISOs and their security teams improve their incident response processes. This involves examining trends. It also extrapolates how a potential attack could impact their organization. Furthermore, understanding how and where they occur can help security and intelligence teams understand their risk profiles. This can potentially prevent them from happening.
In this article, we:
- Define the term “data breach”
- Describe how data breaches occur
- Explain how threat actors operate and the information or access they’re after
- Provide examples of public large-scale data breaches
- Outline defend against a cyber attack, and how to prepare a response plan
What is a Data Breach?
A data breach occurs whenever sensitive data is unintentionally exposed. It also occurs when an unauthorized entity leaks, or steals it. Breach events could range from one to billions of records of breached data. However, over the past few years breach events have begun to expose billions of records containing sensitive data and customer information.
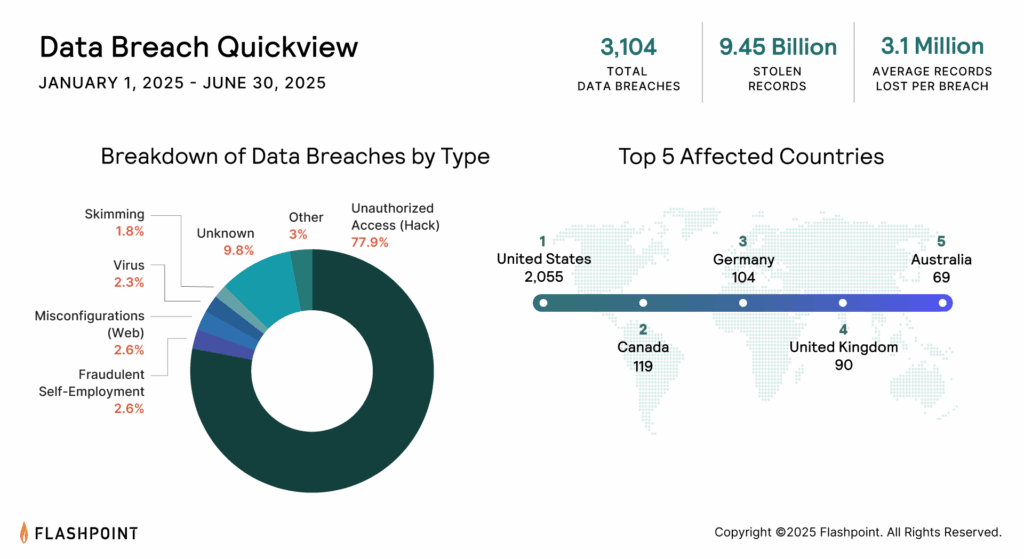
How Do Data Breaches Occur?
“Hacking,” the unauthorized access to systems or services, has been the driving factor for reported breach events. It has been the number one reported breach type for over the past 10 years. Malicious actors use a combination of social engineering techniques. They also exploit vulnerabilities. This is to gain illegal access into an organization’s network.
However, research shows that breaches that have exposed the most records are the result of human error. This stems from poor security controls and unpatched system vulnerabilities. Many impacted organizations are quick to claim that they fell victim to a “sophisticated cyber attack.”
Poor Security Controls Have Been Responsible for Billions of Exposed Records
Misconfigured databases and weak security best practices accounted for approximately 260 data breaches in 2025. Threat actors are continuously scanning the Internet for exposed databases. These databases are available to the masses via search engines and public-facing pages. These databases often have poor password security. They may also lack 2-factor authentication. Threat actors or security researchers often discover them. Threat actors then advertise their existence on illicit forums.
Threat Actors Exploit Vulnerabilities to Gain Illegal Access
On the other hand, malicious actors also scan a potential victim’s network looking for vulnerable assets. They then use that information to turn vulnerabilities into weapons by using exploits. Once compromised, threat actors can either choose to move laterally within the system. They can also install ransomware to steal data.
As such, vulnerability intelligence is critical to reduce risk. This is because vulnerability management processes are dependent on it. However, organizations cannot rely on publicly available sources like CVE or NVD. They are completely unaware of nearly a third of known risk. Security teams will need a comprehensive source of vulnerability intelligence to fix issues effectively. This is because, according to Dark Reading, nearly every application has at least one vulnerability or misconfiguration that compromises security in some way.
What Type of Data do Hackers Steal?
Any kind of private data can be involved in a data breach. However, threat actors often seek personally identifiable information (PII). This is because it can be easily sold on illicit marketplaces. Breached PII often includes:
- Names
- Email addresses
- Passwords
- Addresses
- Date of birth
- Social Security Numbers
- Drivers license numbers
- Credit card information and other financial data
There are some situations where PII is not the main target. In these scenarios, the attacker is usually revealed to be an APT, hacktivist, or some other highly-skilled threat actor. They are after specific information. Such information can include:
- Classified government documents or communications
- Internal business information, such as trade secrets
- Proprietary source code
- Infrastructure data
How Organizations Can Prevent Data Breaches
“Comprehensive and repeatable processes for hardening systems, coupled with periodic audits of controls can substantially reduce the likelihood of a large scale data leak.“
STATE OF DATA BREACH INTELLIGENCE, FLASHPOINT
Prevention is the ideal data breach scenario for any organization. Educating personnel and implementing security best practices goes a long way. This is for cases involving human error, such as misconfigurations and social engineering campaigns.
Security teams also need to ensure that they are patching vulnerabilities regularly. They should especially focus on deployed assets that house sensitive data. Having a comprehensive source of vulnerability intelligence such as Flashpoint’s VulnDB is crucial. Vulnerability Management teams need detailed intelligence that contextualizes risk to their assets. Additionally, VulnDB also gives security teams the ability to predict which vulnerabilities could be used in future ransomware attacks. This empowers them to stop threat actors.
Enterprises should also assess and improve their third-party vendor security. They must make sure that everyone within their supply chain is taking security seriously. In today’s business landscape, data is often being shared between multiple organizations. Recent cyberattacks demonstrate that a weak link in your digital supply chain can introduce a risk gap. This gap can be difficult to detect or address.
The Importance of Incident Response
However, business leaders should not focus solely on pre-emptive measures. Resiliency and having a well-developed incident response plan is just as important. If organizations find themselves compromised, they will need to contain the threat and respond quickly. Effective containment and response strategies can involve:
- Locating, repairing, and securing affected systems
- Reporting the breach to a regulatory authority
- Informing affected individuals
- Rely on cybersecurity and digital forensics experts to gather appropriate threat intelligence to better understand how the system was compromised
- Improving security processes to prevent future attacks
Prevent and Respond to Data Breaches with Flashpoint
Data breaches can have a serious impact on any organization. Data shows that anyone can become a potential victim. Flashpoint Professional Services (FPS) offers a Threat Response and Readiness Subscription. This helps companies prepare for and respond to a ransomware or cyber extortion attack. Organizations will greatly benefit from our newly introduced Ransomware Prediction Model. This is for security teams seeking to get ahead of ransomware events. It provides a Ransomware Likelihood score for over 300,000 vulnerabilities.
Frequently Asked Questions (FAQ)
Q. What is a data breach and how does Flashpoint define it?
A. A data breach occurs when sensitive data is exposed or stolen by an unauthorized entity. Flashpoint provides intelligence that contextualizes the breach by identifying the exposed records, tracking where the data is sold, and detailing the threat actor’s methods.
Q. How does Flashpoint’s intelligence prevent data breaches?
A. Flashpoint prevents data breaches by providing comprehensive threat intelligence and VulnDB. It gives teams a comprehensive view of vulnerabilities—including the nearly one-third missed by public sources like NVD—and the Ransomware Prediction Model, which predicts which vulnerabilities are most likely to be used in future attacks.
Q. What services does Flashpoint offer for incident response after a breach?
A. Flashpoint offers Flashpoint Professional Services (FPS), which includes the Threat Response and Readiness Subscription. This service helps organizations prepare for and respond quickly to cyber extortion, ransomware, and data breach incidents to minimize financial loss and recovery time.
Related Resources
Get the latest news and insights delivered to your inbox.
Interested to see top news from Flashpoint hit your inbox directly? Subscribe to our newsletter to receive curated content on a regular basis.



