You’re an intelligence analyst and your team has just received an alert for a potential security breach. You need fast access to relevant data to generate threat intelligence and initiate a response, but your tooling is returning a sea of false positives that’ll take ages to navigate.
Whether working in the public or private sector, intelligence analysts need to support the generation of timely, comprehensive threat intelligence. This enables security teams and governments to make faster, more informed decisions in response to risk—and ultimately avoid or reduce damage to people, infrastructure, and other vulnerable assets.

Assessing Geopolitical Risk
Whitepaper: How OSINT tools can address current intelligence challenges.
But when it comes to gathering online data, analysts must filter a vast amount of information to find what’s relevant. When analysts are overwhelmed with false positives, they sacrifice the speed-to-information and context required to protect assets—not to mention wasting time and resources.
But there’s good news: as an analyst you can address these gaps by exercising your Boolean logic chops.
In combination with the right data discovery tooling, these skills can go a long way to streamline your search results and support faster delivery of high-quality intelligence. As an intelligence analyst or OSINT investigator, how can you build stronger searches with Boolean rules?
Applying Boolean operators: The basics
Whether you’re using a standard search engine like Google or gathering OSINT through a sophisticated threat intelligence tool, Boolean rules are crucial for refining your search results. These rules incorporate three basic operators: AND, OR, and NOT:

These Boolean rules become even more powerful when combined with brackets (). For example, if you’re looking for content about theft in Victoria, BC, you might structure your Boolean string like this:
This allows you to find results that account for spelling variations or different word combinations that could be relevant to your search. Depending on the search tool you’re using, other operators may be supported and can help you further refine your Boolean strings. Here are a few commonly supported operators to practice:
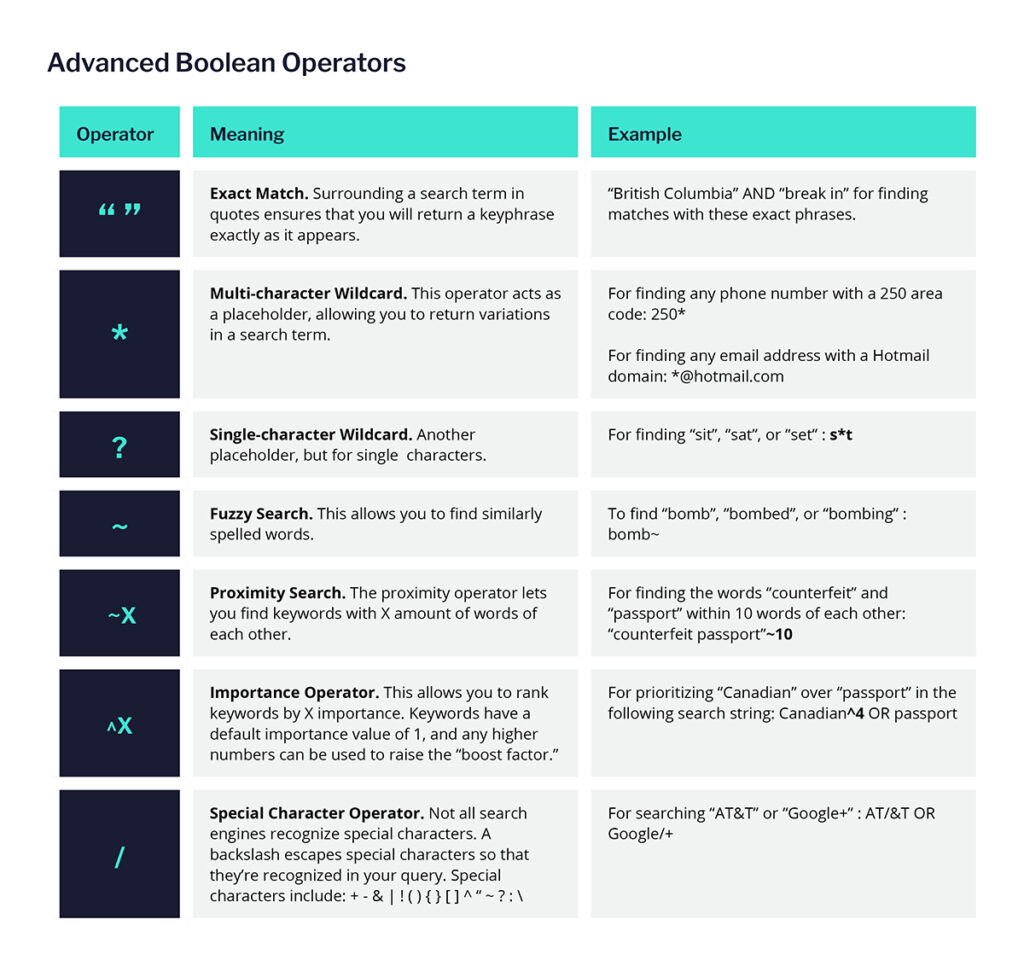
Maximizing Boolean rules for your investigation
Simply knowing how to apply Boolean rules isn’t enough. Like anything, it takes practice—and online Boolean guides aren’t always the best at providing analyst-specific support for security and intelligence use cases. Here are some tips to help you maximize your search strings and return more relevant results.
Keyword research
Rather than using broad or generic search terms (e.g. “malware,” “human trafficking,” etc.), do some keyword reconnaissance to get more relevant results. Start by Googling the topic and researching news, intelligence briefings, and think tank articles. Make sure you understand the language and culture relevant to your target topic. Some factors to consider in your keyword selection:
- Are there any hashtags associated with this topic?
- Could the target keywords be relevant in other languages or vary depending on the region? For example, the language used by human traffickers will be very different in the US than in Africa.
- Are there key locations for a specific topic? Include relevant location names like airport hashtags and city names, or granular locations like neighborhoods and building names.
- Are there slang terms or spelling variations prevalent in the target content? For example, extremist groups might use racial slurs, coded language, or nicknames to target individuals or groups rather than common names.
Start simple
Once the goal of your search is clear and you have a solid keyword list, start with short, simple Boolean strings. If this returns too much noise, add more operators, keywords, or parameters to narrow your search from there.
Use results to build your keyword list and guide your investigation
As you review your search results, keep your eye out for hashtags, terms, identifiers, and other keywords that can be validated to support your investigation. Search tools that provide analytics like top hashtags and word clouds are useful for finding this information. Also, take note of any data sources that are more relevant than others for your topic of interest.
Incorporate additional parameters
Search engines and paid search tools often include other parameters, such as the date published range or the data source type (e.g. deep vs. dark web). Combine these with your Boolean search strings when relevant to streamline results.
Reduce false positives
If you’re seeing false positives with a common denominator, such as a common site URL, username, or irrelevant keyword, use the NOT (-) operator to eliminate it from your results.
Make multilingual searches consistent through Boolean strings
For example, searching trafficking AND “торговля людьми” is ineffective because results are unlikely to include both equivalent English and Russian terms. If you are looking for results that could include multiple languages, ensure that your Boolean query reflects that (e.g. trafficking OR “торговля людьми”).
Finished intelligence reports are only as good as the raw data they are built from. Without the ability to quickly separate noise, your team could be missing out on critical context—or sacrificing speed-to-information in the laborious quest for relevant data.
This is why mastering Boolean rules—and combining those skills with robust data discovery tooling—is essential for intelligence analysts. Not only will you save time, but you’ll also generate higher-quality intelligence and support timely, more informed security decision-making.


