Blog
Preventing Future Ransomware Attacks With VulnDB
Flashpoint Vulnerability Intelligence leverages a ransomware prediction model (Ransomware Likelihood score) to proactively identify and prioritize the vulnerabilities most likely to be exploited by ransomware threat actors. This solution is crucial because traditional CVE/NVD data is unaware of nearly a third of known risk and famously lacks the necessary context and advanced metadata to effectively triage and prevent cyber extortion events.

Since ransomware’s introduction to the world in 1989, it has evolved into a devastating weapon that is wielded by threat actors and Advanced Persistent Threats (APTs). According to the CyberSecurity Infrastructure Security Agency (CISA), 14 of 16 critical US infrastructure sectors have experienced a ransomware attack, and in a recent FBI report, ransomware events increased by 62 percent compared to 2021.
Even though the US government has increased efforts to improve security in federal agencies and in the private sector, ransomware continues to wreak havoc. Further demonstrating the pervasive and lucrative business of ransomware is a recent report from the US Treasury, which finds that ransomware-related payments cost banks $1.2B in 2021, nearly double the previous year.
This prompts the question: How can organizations get in front of ransomware attacks and prevent them in the first place?
The Inadequacy of Public Vulnerability Data (CVE/NVD) for Ransomware Defense
Cyber extortion events can be prevented if you have the right intelligence—timely, relevant, actionable data that can bolster an organization’s ability to defend its attack surfaces, such as vulnerabilities. Well-versed threat actors and APTs are actively exploiting vulnerabilities found in end-user software and third-party libraries and dependencies to conduct their ransomware campaigns. Therefore, it’s crucial for vulnerability management teams to identify vulnerable assets, prioritize vulnerabilities, and then inform security teams to patch them in a timely manner.
However, organizations relying on publicly-available vulnerability data will be unable to triage effectively since CVE/NVD is unaware of nearly a third of known risk. In addition, the public source infamously lacks context and actionable details—ultimately causing security teams to squander valuable resources.
CISA does on occasion detail APT activity and knowing which vulnerabilities have been used in previous attacks is valuable. However, just having that knowledge is neither actionable nor timely. To collect that data, an organization must first become the victim of a ransomware event, and then the attack must be disclosed. Only then can other organizations take action.
Instead, there is a better way to proactively take measures against future ransomware campaigns—comprehensive vulnerability intelligence, and Flashpoint’s new tool that is dedicated to help prevent ransomware attacks.
Introducing Flashpoint’s Predictive Vulnerability Ransomware Model (Ransomware Likelihood Score)
Flashpoint’s vulnerability intelligence research team has created a first-of-its-kind ransomware prediction model—that is capable of predicting the likelihood that a particular vulnerability would be used in ransomware operations. For over 300,000 vulnerabilities, Flashpoint now provides our Ransomware Likelihood score. This capability can only be found in Flashpoint products, such as VulnDB and Ignite, the most comprehensive source of vulnerability intelligence available.
This score is a rating that estimates the similarity between a vulnerability and those known to be used in ransomware attacks. To ensure our customers have the most up-to-date information, a given rating can change as our intelligence team learn more about a vulnerability and uncover additional vulnerabilities used in ransomware attacks.
Equipped with Flashpoint’s robust metadata and numerous prioritization metrics, Vulnerability Management teams are now equipped with the information needed to better prioritize and take action on the vulnerabilities likely to be used in ransomware and other attacks.
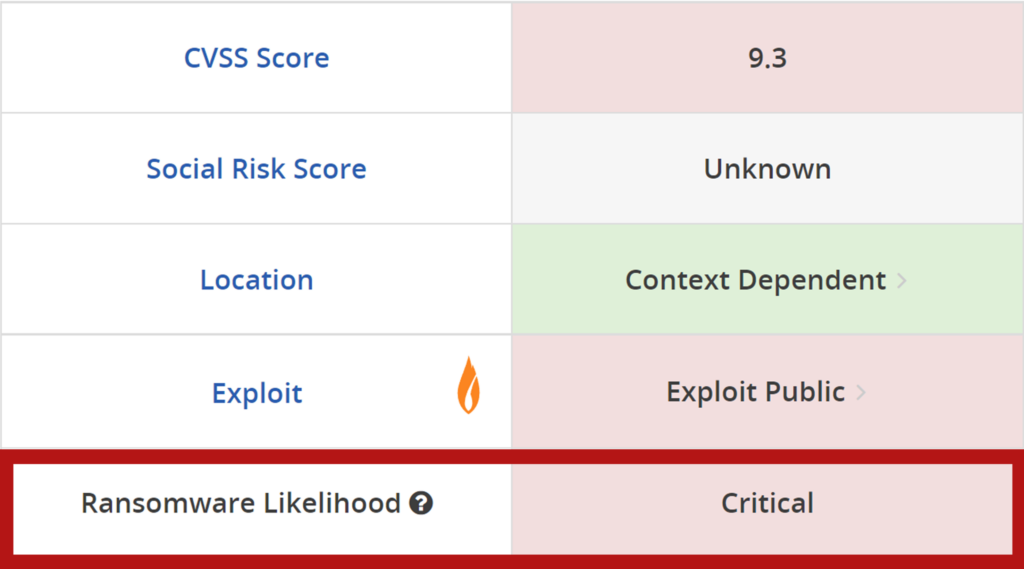
The model takes a vulnerability, as well as newly disclosed issues—using predictive analysis to determine the likelihood that it will be used in future ransomware operations. With this information, security teams can prioritize remediating those vulnerabilities first, better protecting their organization as a whole.
VulnDB: The Ultimate Vulnerability Intelligence Solution with Comprehensive Coverage
Combined with the added context delivered by the Flashpoint Intelligence Platform—including primary source data across illicit communities, threat actors TTPs, and malware families, VulnDB becomes the go-to source for vulnerability intelligence and management.
VulnDB’s independently researched vulnerability database covers over 300,000 vulnerabilities (of which 96,000+ are not included in CVE/NVD) and 60+ fields of advanced metadata such as exploitability, attack location, solution information, and now, ransomware likelihood.
With VulnDB’s best-in-class vulnerability intelligence, Flashpoint gives organizations the data and insights needed to detect, prioritize and remediate the vulnerabilities that matter most to their organization.
Best-in-class vulnerability intelligence

Get Flashpoint on your side. To learn more about Flashpoint’s ransomware prediction model and VulnDB, reach out for a free trial.
VulnDB and Ransomware Prevention FAQs
Q: What is Flashpoint’s “Ransomware Likelihood Score”?
A: The Ransomware Likelihood Score is a first-of-its-kind feature in VulnDB created by Flashpoint’s research team. It uses predictive analysis to determine the probability that a specific vulnerability (from over 400,000 tracked) will be leveraged and used in future ransomware operations, allowing security teams to prioritize remediation proactively.
Q: How much more comprehensive is VulnDB compared to public sources like CVE/NVD?
A: VulnDB is significantly more comprehensive, covering over 400,000 vulnerabilities, which includes 105,000+ vulnerabilities not contained in CVE/NVD. This extensive coverage means organizations relying solely on public data are missing nearly a third of known risk.
Q: Why can’t vulnerability management teams effectively triage ransomware risks using only CVE/NVD data?
A: Traditional data sources like CVE/NVD are ineffective for ransomware triage because they lack context and actionable details. This forces security teams to squander valuable resources on non-critical threats and prevents them from proactively identifying the vulnerabilities that threat actors are actively exploiting in ransomware campaigns.

