The Israel-Hamas War, sometimes referred to as the Israel-Gaza War, poses crucial questions regarding the region’s future stability— especially when considering the intricate interplay of cyber, physical, and geopolitical security and intelligence challenges. In this article we delve into the multifaceted, ever-evolving conflict landscape, with a goal of decoding the conflict’s intricate dynamics, including the nexus of cyber threats, hacktivism, military operations, and broader geopolitical implications.
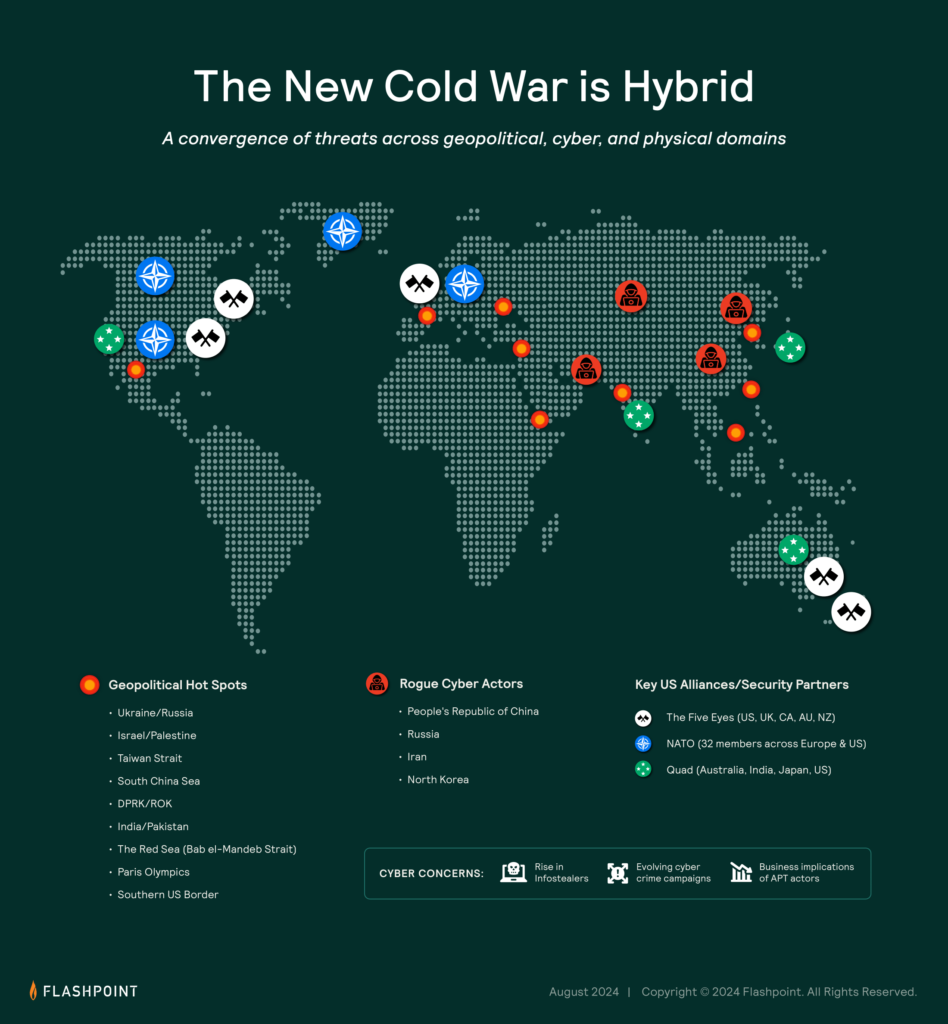
For intelligence professionals, security experts, policymakers, and anyone invested in comprehending this complex conflict, our insights aim to keep you informed as the war unfolds, leveraging our intelligence to deliver clarity amidst the chaos.
Timeline of the Israel-Hamas War
Tracing Decades of Israel-Gaza Relations
The attack by Hamas on Israel on October 7 took both Israel and the world by surprise, especially given its scale and the fact it went undetected by Israel’s intelligence. However, the roots of this conflict stretch back decades.
Historical Echoes
The modern state of Israel was established in 1948, amid aspirations for a Jewish homeland and in the wake of the Holocaust. Its creation, however, led to the displacement of many Palestinians, a significant event referred to as the Nakba or “catastrophe” by Palestinians.
In 1967, after the Six-Day War, Israel occupied the Gaza Strip, a territory that had been under Egyptian administration. The 1973 Middle East war—known as the Yom Kippur War because of its conjunction with the Jewish holiday—was a significant event in Israeli-Arab relations, with coordinated attacks on Israel by Egypt and Syria, and it remains a poignant reminder of the region’s volatile history.
Hamas emerged in 1987 as a resistance movement against Israeli presence. In 2005, Israel unilaterally withdrew from Gaza but maintained control over its borders and airspace. A year later in 2006, Hamas’s electoral victory led to its control of the Gaza Strip after clashes with Fatah, another major Palestinian faction. Since then, the Gaza Strip has been a flashpoint for conflicts between Israel and Hamas, with both sides having deep-seated grievances.
Since then, there have been several escalations of violence between Israel and Hamas. Israel cites concerns over rocket fire from Gaza and the threat posed by tunnels leading into Israel, leading to military operations in the territory. On the other hand, Palestinians in Gaza have faced blockades and frequent military incursions, leading to significant humanitarian concerns.
The relationship between Israel and Hamas in Gaza is emblematic of the broader Israeli-Palestinian tension, which remains one of the world’s most protracted and controversial disputes.
A Calculated Date
The October 7 attack on Israel marked nearly 50 years to the day of the outbreak of the Yom Kippur War, and coincided with the Jewish holiday Shemini Atzeret. The unexpected attack resulted in hundreds of casualties and numerous hostages. Over 2,000 rockets were fired into Israel, causing significant casualties and prompting Prime Minister Benjamin Netanyahu to declare war on Hamas, mobilizing the military and reserves.
Shortly after the attack, we held a webinar to detail the historical context, outline the events of October 7 and the days following, and answer questions related to cyber activity, potential threats, and more.
Militant and Terrorist Groups Involved in the Israel-Gaza War
Although Hamas led the initial assault on Israel, evidence shows that other militant and terrorist groups worked with Hamas. The following groups have been linked to Hamas’ first attack on October 7:
- Izz al-Din al-Qassam Brigades (كتائب الشهيد عز الدين القسام)
- Palestinian Islamic Jihad (الجهاد الإسلامي الفلسطيني)
- Al-Aqsa Martyrs Brigade (كتائب شهداء الأقصى)
- Democratic Front for the Liberation of Palestine (الجبهة الديمقراطية لتحرير فلسطين)
- Palestinian Mujahideen Movement (حركة المجاهدين الفلسطينيين)
- Popular Resistance Committees (لجان المقاومة الشعبية)
Flashpoint will update this list as the situation in Israel, Gaza, and the Middle East develops.
Digital Frontlines: OSINT in the Israel-Hamas War
Open source intelligence (OSINT) continues to be a driving force in modern warfare. If harnessed, publicly available information (PAI) can bring real-time insights into global events—especially the Israel-Hamas War.
Like with the Russia-Ukraine War, we are already witnessing a battlefield taking place on the digital front. An increasing amount of cyber threat actors are joining the fray, unleashing a flurry of DDoS attacks and ransomware against both Israeli and Hamas systems.
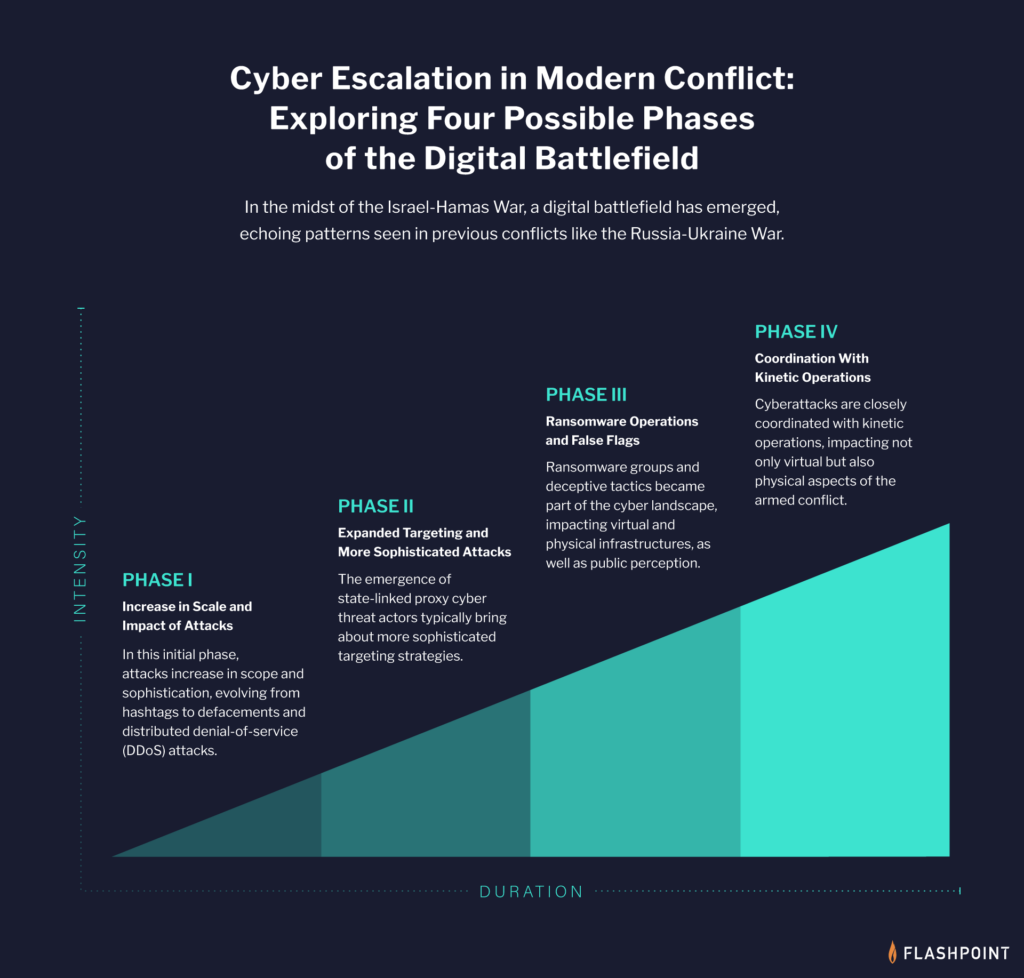
This is what we’ve seen unfolding so far in the digital battlefield:
Telegram’s Role in the Israel-Gaza War
Open source intelligence platforms such as Telegram are proving to be indispensable both for militant groups and intelligence professionals. As seen in the Ukraine-Russian War, Telegram is being used as a rallying point for Hamas and the PIJ, where their members are sharing propaganda and real-time updates related to the war effort. On the opposite side, intelligence operators are monitoring their Telegram channels in attempts to circumvent militants and document war crimes.
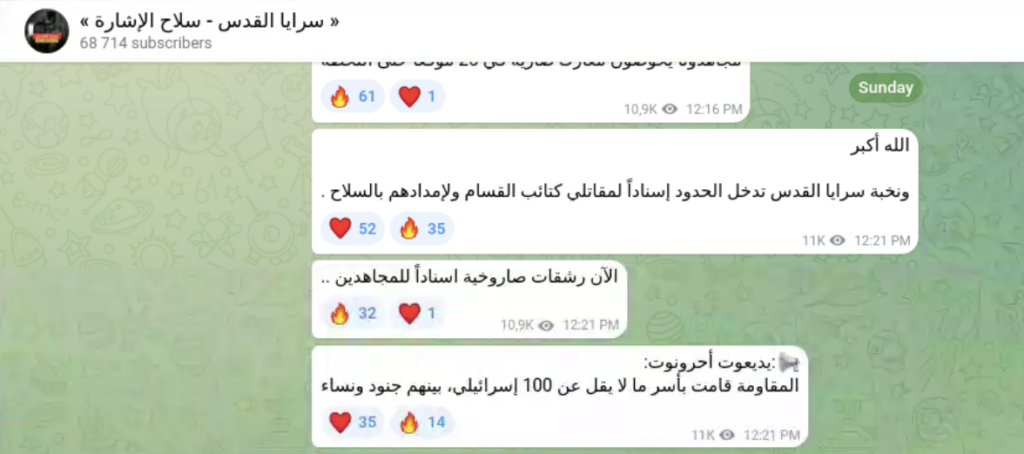
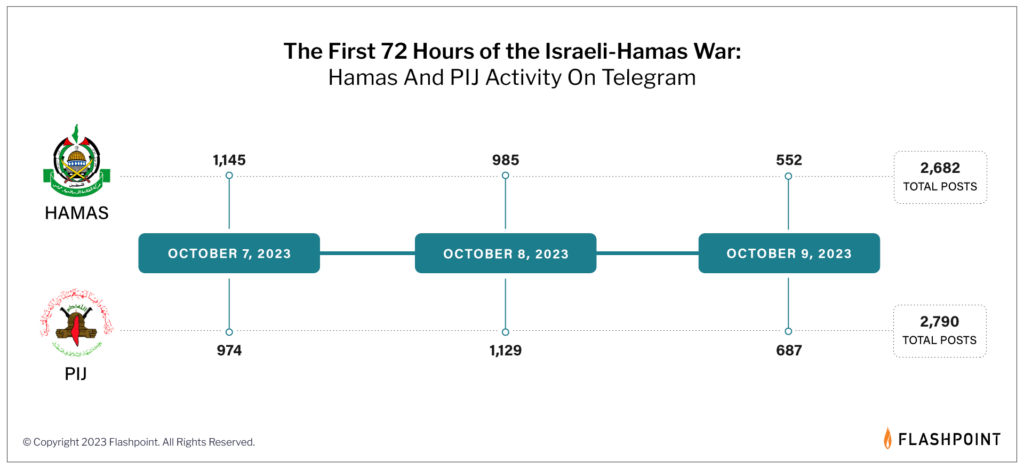
In just the first 72 hours of the Israel-Hamas War, Flashpoint found that a total of 5,472 Telegram posts were shared between multiple channels operated by Hamas and the PIJ:
Telegram Bans Hamas and Izz al-Din al-Qassam Brigades
On October 25, Telegram announced that they had banned Hamas and its militant wing from its platform for users on Android operating systems. This follows ongoing efforts of major social media platforms to remove misinformation and violent, disturbing content involving the Israel-Hamas war.
Hamas and its supporting groups are instructing sympathizers to download alternative or modified versions of the Telegram app in hopes of circumventing the ban. They are also advising users to use VPNs and virtual machines to bypass censorship.
Potential and Real Effects of Hamas’ Telegram Ban
Telegram’s ban of Hamas and its militant wing may introduce some short and long term effects. The first being the potential growth of independent apps and alternate encrypted chat platforms such as Rocket.Chat and Chirpwire.
In addition, switching to new platforms may attract new recruits and sympathizers who were not previously engaged, potentially expanding Hamas’ global reach. However, Telegram’s ban has created an immediate replacement: Al-Qassam Media.
Al-Qassam Brigades Push Mobile Android App
On October 26, 2023, Izz al-Din al-Qassam Brigades encouraged supporters to download the “trial version” of a mobile application called Al-Qassam Media, available for some mobile operating systems.
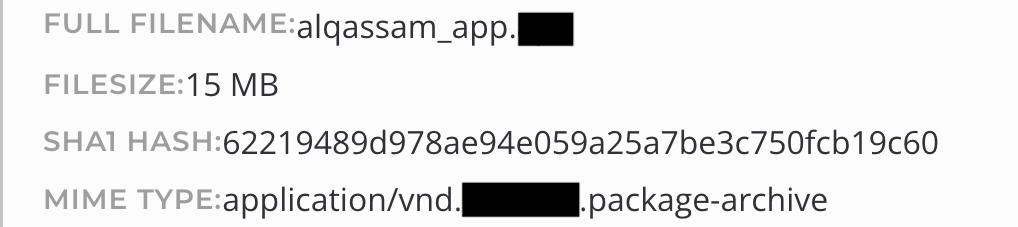
Hamas will very likely persist in promoting the new application as an alternate means of communication as its Telegram chats and channels continue to be banned. At this time, the app appears to be strictly mobile. Therefore, the shift in communications to this application may make it difficult for analysts to monitor and collect Hamas-related communications.
Hacktivism in the Israel-Hamas War
The strained and nuanced nature of the Israel Palestine conflict has not only divided the public, but cybercriminals as well—with multiple hacktivist groups siding with, or against Israel—choosing to support Hamas or the general Palestinian territories due to opposition of Israel’s diplomatic partners.
Dozens of pro-Israel and pro-Hamas hacktivist groups are active online and communicating using social media channels such as Telegram and X (formerly Twitter). While it is unclear how many groups are actively coordinating attacks due to the conflict, prominent hacktivist groups, including Anonymous Sudan and Killnet (see below), have announced their involvement in cyberattacks targeting institutions in both Israel and the Palestinian territories.

Hacktivist Groups that are Pro-Israel or Anti-Hamas
At this time, the following hacktivist groups have declared support for Israel, or have aligned themselves against Hamas:
- GonjeshkeDarande
- INDIAN CYBER FORCE
- UCC Team
- Garuna Ops
- SilentOne
- IT ARMY of Ukraine
- Termux Israel
- Anonymous Israel
- Kerala Cyber Xtractors
- GlorySec
- Team NWH Security
- Anonymous India
- Dark Cyber Warrior
- Gaza parking lot crew
- ICD – Israel Cyber Defense
- Anomymiss
- Silencer_of_evil
Hacktivist Groups Pro-Hamas or Anti-Israel
The following groups have announced their support for either Hamas, the Palestinian territories, or are anti-Israel:
- Killnet
- Killnet launched a new Telegram channel dedicated to Palestine-related activities and “standing against Israel and anyone who supports the Zionist Entity.”
- AnonymousSudan
- AnonGhost
- UserSec
- Anonymous Russia
- Anonymous Indonesia
- Mysterious Team Bangladesh
- Anonymous Morocco
- Ganosec Team
- Moroccan Black Cyber Army
- Muslim Cyber Army
- GhostClan
- Eagle Cyber Crew
- Team Herox
- Arab Anonymous Team
- light in the dark


