Over the past seven years, Flashpoint has observed a significant rise in the use of infostealer malware. Their simplicity, vast availability, and low costs have made them extremely popular among threat actors, making infostealers an increasingly primary vector for ransomware and other high-impact data breaches. Therefore, it is crucial for organizations to protect themselves against this growing threat. In this blog, we explain the risks posed by infostealer malware and outline the essential steps security teams can take to ensure the integrity of sensitive data.

The Evolution and Rise of Stealer Malware
Learn what stealers are, how they work, and what malicious actors are doing with compromised data.
Understanding Infostealer Malware
Infostealers are a type of malware designed specifically to harvest sensitive information, such as login credentials (commonly referred to as “logs”) from infected systems. Logs are incredibly valuable for threat actors—especially those related to third-party software-as-a-service applications such as Salesforce, Slack or Microsoft Office 365—since compromised credentials can allow them to infiltrate and move laterally within systems.
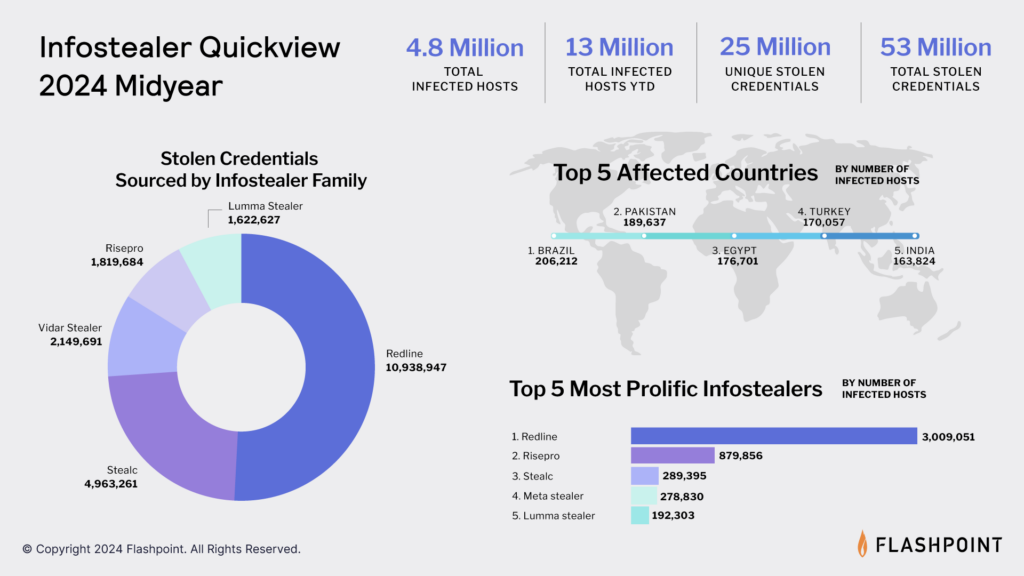
The Infostealer Lifecycle and TTPs
Even one compromised credential can result in a data breach or cyberattack. For example, in January 2024, a major European telecommunications company suffered a massive network outage that impacted around half of its network’s traffic. The root cause was traced to a single weak password that was exposed by infostealer malware.
The Infostealer Lifecycle
- Infection: Information-stealing malware was used to expose login credentials, including a weak password which was sold on underground markets.
- Exposure: Sold credentials included access to the IP network coordination center (RIPE) account and a critical database containing IP addresses and their owners in Europe, the Middle East, and Central Asia.
- Infiltration and escalation: The threat actor(s) that purchased these credentials leveraged the weak password to log in to the organization’s RIPE account and initiated further malicious activities. MFA or 2FA was not enabled on the compromised account.
- Attack: Malicious actors caused a massive network outage which impacted around half of its network traffic.
Infostealer TTPs
Depending on the strain of infostealer, threat actors can adapt their TTPs to bypass security measures, making it imperative for organizations to implement comprehensive defenses. The following tags from MITRE ATT&CK helps define the usual TTPs affiliated with information-stealing malware:
- Valid Accounts (T1078): Obtained through information stealer logs, either in Telegram channels, subscription services, or venues like Russian Market.
- Command and Scripting Interpreter (T1059): Executes commands to deploy the malware.
- Obfuscated Files or Information (T1027): Avoids detection through obfuscation techniques.
- Credentials from Password Stores (T1555): The information-stealing malware extracts passwords from stores.
- Query Registry (T1012): The information-stealing malware gathers additional system and user information.
- Data from Information Repositories (T1213): The attacker collects data from various information repositories.
- Exfiltration Over Web Service (T1567): The data is exfiltrated to an external web server controlled by the attacker.
- Data Encrypted for Impact (T1486): The exfiltrated data is encrypted or compressed before exfiltration.
Protecting Against Infostealer Malware
Step 1: Implement Targeted Security Measures
One of the most effective ways to protect against infostealers is to ensure that specific, targeted security measures are in place. This is even more important as organizations increasingly rely on third-party services and platforms. The following best practices will significantly mitigate risk posed by infostealers:
- Use strong passwords and multi-factor authentication:
Adds an extra layer of security, making it more difficult for attackers to gain unauthorized access. - Rotate or update credentials:
Regularly changing passwords limits the opportunity for attackers to exploit stolen credentials. - Install network access controls:
Only allow access from trusted locations or specific IP ranges. - Monitor for the use of compromised session cookies:
Deploy monitoring tools and educate employees on the importance of logging out from sessions and clearing browser cookies. - Monitor third-parties or contractors:
Regularly review and audit access permissions. Ensure that contractors are beholden to the same security standards and conduct regular security assessments.
While many of these best practices are well established and generally implemented, security teams must remember that compliance is only the first step. For example, some systems and software may not require MFA or prompt users to update passwords. However, it is critical that organizations mandate the use of MFA or 2FA and routinely update credentials. Even though these steps are basic, threat actors often infiltrate victim systems by exploiting these gaps, even in larger organizations.
Step 2: Monitor for Stolen Logs
After ensuring that foundational protections are in place, organizations looking to protect against infostealer malware need to monitor illicit marketplaces for any stolen logs that are alleged to stem from your organization or associated third parties. However, without a comprehensive source of threat intelligence, doing so will be a major challenge—as there are tens of thousands of Telegram channels, subscription log services, and log shops.
Flashpoint has observed multiple instances of malicious actors attempting to gain access to organizations via the following domains:
- 1password.com
- atlassian.net
- greenhouse.io
- okta.com
- salesforce.com
- service-now.com
- sharepoint.com
- slack.com
- splunkcloud.com
- zendesk.com
- zoom.us
Using Flashpoint, organizations can inventory their infrastructure and share any internal domains with our analysts. Doing so creates custom alerts that notifies security teams of any potential incidents leveraging Flashpoint’s massive collections.
Step 3: Proactively Acquire Logs and Remove Them from Illicit Marketplaces
In addition to monitoring, organizations may want to consider proactively acquiring logs themselves and removing them from illicit marketplaces. Using Flashpoint’s Requests for Information (RFI) service, organizations can request our intelligence analysts to acquire the listing on their behalf and take precautions to remove it from log shops.
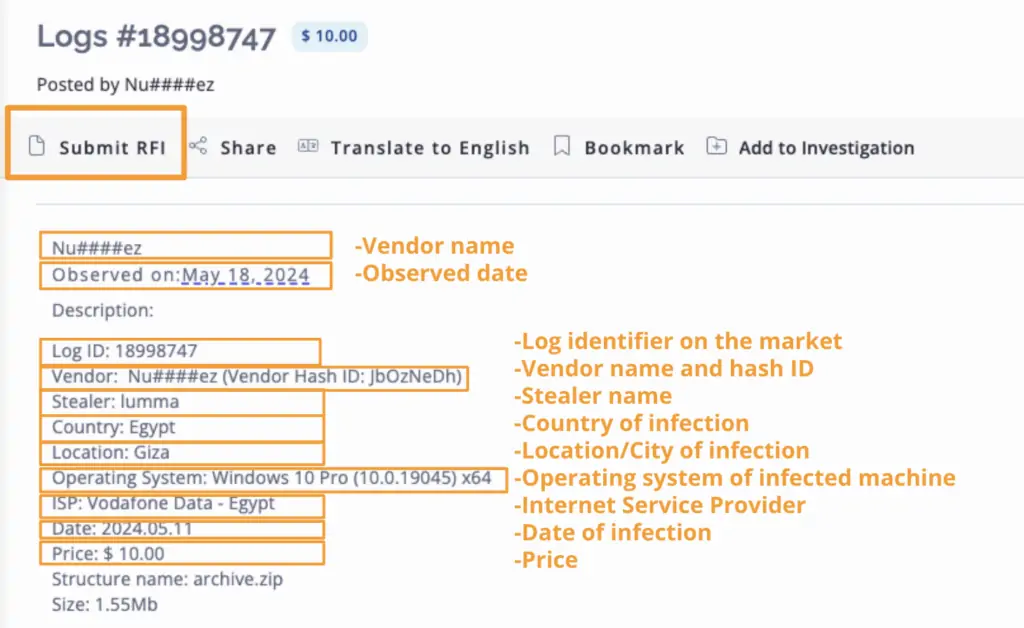
Step 4: Leverage Insights to Stay Ahead of Potential Threats
Ultimately, organizations need to stay informed about emerging infostealer trends and techniques. New variations of infostealers are constantly being advertised on illicit marketplaces and each variant improves its ability to bypass defensive measures.
Leveraging a comprehensive source of threat intelligence like Flashpoint Ignite provides security teams with unparalleled visibility into the threat landscape. Through a single easy-to-use platform, organizations gain insight into the deep and dark web, open source intelligence, vulnerabilities, and breach data. Armed with Flashpoint’s massive collections and finished intelligence reports, security teams can stay ahead of potential threats.
Protect Yourself Against Infostealer Malware Using Flashpoint
Infostealer malware poses significant risks to organizations, but with the right security measures informed by the best data and intelligence, these risks can be mitigated. By following these steps, security teams can build a resilient defense against infostealers, ensuring robust protection for critical assets. Sign up for a demo to learn how you can better protect yourself today.



